
India's social enterprise support is characterized by a diverse and dynamic support ecosystem, crucial in fostering innovation and growth in social entrepreneurship. This ecosystem comprises incubators, accelerators, co-working spaces, policymakers, and various forums and networks.
These elements work synergistically to support social enterprises comprehensively, helping them evolve from ideation to the investment stage. This article delves into the various components of this ecosystem, exploring their roles, geographic distribution, and the emerging trends that shape the social enterprise sector in India.
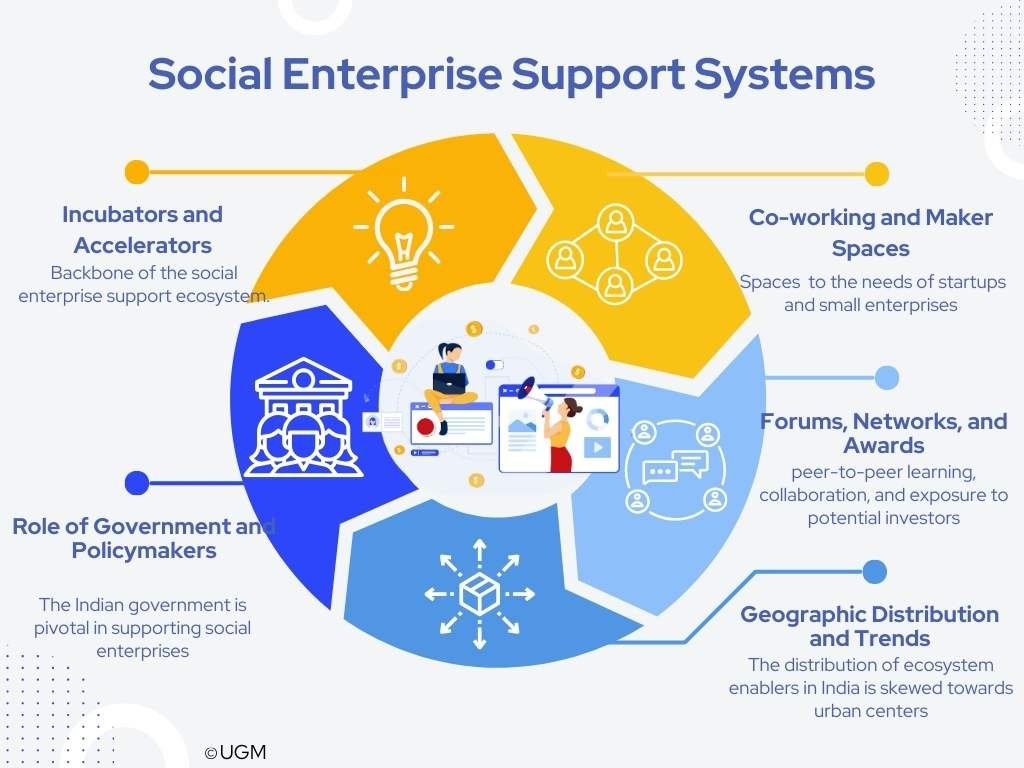
Incubators and accelerators form the backbone of the social enterprise support ecosystem. They offer various non-financial support services, including mentoring, business planning, and networking opportunities. Many also provide financial assistance in the form of seed funding. These entities are critical in helping social enterprises navigate the challenging journey from concept to viable business.
According to a report by NASSCOM, India is home to over 190 active business incubators and accelerators. These are distributed across various entities, such as academic institutions, corporate organizations, government bodies, and private enterprises.
Most of these incubators are in major metropolitan areas like Mumbai, Bengaluru, and Delhi/NCR. However, there is a growing trend of establishing incubators in Tier II and Tier III cities to tap into the burgeoning entrepreneurial spirit in these regions.
These smaller cities offer lower operational costs, making them attractive to new enterprises with limited financial resources. Where we need to think to establish and grow more social enterprise support systems.
Incubators such as Dasra, Villgro, and UnLtd India are notable for their comprehensive support across various sectors, including healthcare, education, agriculture, and clean energy. They provide funding, hands-on support, infrastructure, and access to a vast network of experts and investors.
Co-working and maker spaces are another vital component of the social enterprise support ecosystem. These spaces provide affordable, flexible office solutions that cater to the needs of startups and small enterprises.
They offer essential amenities such as internet access, meeting rooms, administrative support, and value-added services like legal and accounting assistance.
Co-working spaces are predominantly found in metropolitan areas but gradually expand to smaller cities. This expansion is driven by the need to support the growing number of startups emerging from these regions.
Examples of co-working space providers include 91Springboard, WeWork, and Innov8, which offer a collaborative environment conducive to innovation and networking.
The Indian government is pivotal in supporting social enterprises through various policies, schemes, and development initiatives. Several government departments and agencies, such as the Department of Biotechnology and the Ministry of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSME), have established incubation programs to nurture startups.
For instance, BIRAC (Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council) supports life sciences startups through its BioNEST program, providing infrastructure, mentorship, and funding.
Government-backed incubators often collaborate with academic institutions and research organizations to leverage their expertise and resources. This collaboration helps rapidly prototype ideas and products, providing startups with access to cutting-edge technology and research facilities. Hence this role is vital for overall social enterprise support system.
Forums and networks are essential in providing platforms for peer-to-peer learning, collaboration, and exposure to potential investors. Events like the TATA Social Enterprise Challenge, Sankalp Forum, and National Entrepreneurship Network bring together social entrepreneurs, investors, and policymakers to discuss challenges, share experiences, and explore growth opportunities.
Awards and recognition programs also motivate social enterprises by acknowledging their contributions and giving them visibility and credibility. These platforms are crucial for networking and accessing resources that can help scale their impact.
The distribution of ecosystem enablers in India is skewed towards urban centers due to better infrastructure and access to funding and business development networks. However, a noticeable shift towards decentralization has occurred, with more support systems being established in smaller cities and towns. This trend is driven by the need to support the increasing number of social enterprises emerging from these regions.
Initiatives like Incuspaze, which has centers in cities like Lucknow, Jaipur, and Indore and plans to expand to 30 Tier II cities, exemplify this trend. Similarly, the BioNEST incubator at the University of Hyderabad caters to the life sciences startups in and around the region, showcasing the growing reach of support systems beyond metropolitan areas.
While India's social enterprise support ecosystem is robust, it faces several challenges. These include the need for more tailored support services for different stages of enterprise growth, greater access to funding, and enhanced infrastructure in smaller cities.
Additionally, there is a need for more collaboration between various ecosystem enablers to provide holistic support to social enterprises.
Despite these challenges, the social enterprise support ecosystem presents significant opportunities. The growing interest in social entrepreneurship, coupled with supportive government policies and an increasing number of ecosystem enablers, provides a fertile ground for the growth of social enterprises in India.
The expansion of co-working spaces and the growing involvement of academic institutions in incubation activities are positive trends that bode well for the future of social entrepreneurship in the country.
1. What is a social enterprise?
A social enterprise is a business that aims to solve social, cultural, or environmental issues through innovative solutions while maintaining financial sustainability.
2. How do incubators support social enterprises?
Incubators provide non-financial support such as mentoring, business planning, and networking opportunities. Many also offer financial assistance in the form of seed funding.
3. What role does the government play in supporting social enterprises in India?
The government supports social enterprises through various policies, schemes, and development initiatives. Departments like the Department of Biotechnology and the Ministry of MSME have established incubation programs to nurture startups.
4. What are co-working spaces, and how do they help social enterprises?
Co-working spaces provide affordable, flexible office solutions with essential amenities and value-added services. They create a collaborative environment conducive to innovation and networking.
5. Are there any specific forums or networks for social enterprises in India?
Several forums and networks, such as the TATA Social Enterprise Challenge, Sankalp Forum, and National Entrepreneurship Network, provide platforms for peer-to-peer learning, collaboration, and exposure to potential investors.
6. What challenges are faced by India's social enterprise support ecosystem?
Challenges include
7. What are the opportunities for social enterprises in India?
The growing interest in social entrepreneurship, supportive government policies, and an increasing number of ecosystem enablers present significant opportunities for the growth of social enterprises in India. Even as you read through this article , we recomend establishing your own social enterprise support system for your district or city.
By understanding and leveraging the social enterprise support ecosystem, we can contribute to and benefit from the growth and impact of social enterprises in India. This collaborative effort can lead to sustainable development and positive change nationwide.